Neurorehabilitation Explained: Advanced Recovery for Brain & Nerve Disorders

Neurorehabilitation is the specialized process of helping patients recover from nervous system injuries (stroke, TBI, spinal cord injury) or manage progressive neurological diseases (Parkinson’s). It combines medical expertise with cutting-edge technology (robotics, brain mapping) and compassionate care. The goal is not just medical stability, but the restoration of function, independence, and dignity. Visionaries like Dr. Sharan Srinivasan are leading this field by integrating holistic care with advanced science.
The New Era of Recovery
In the past, a severe stroke or brain injury often meant a life of permanent dependency. Today, the field of neurorehabilitation is rewriting that narrative. It operates on the principle of Neuroplasticity—the brain's incredible ability to reorganize itself, form new connections, and compensate for injury.
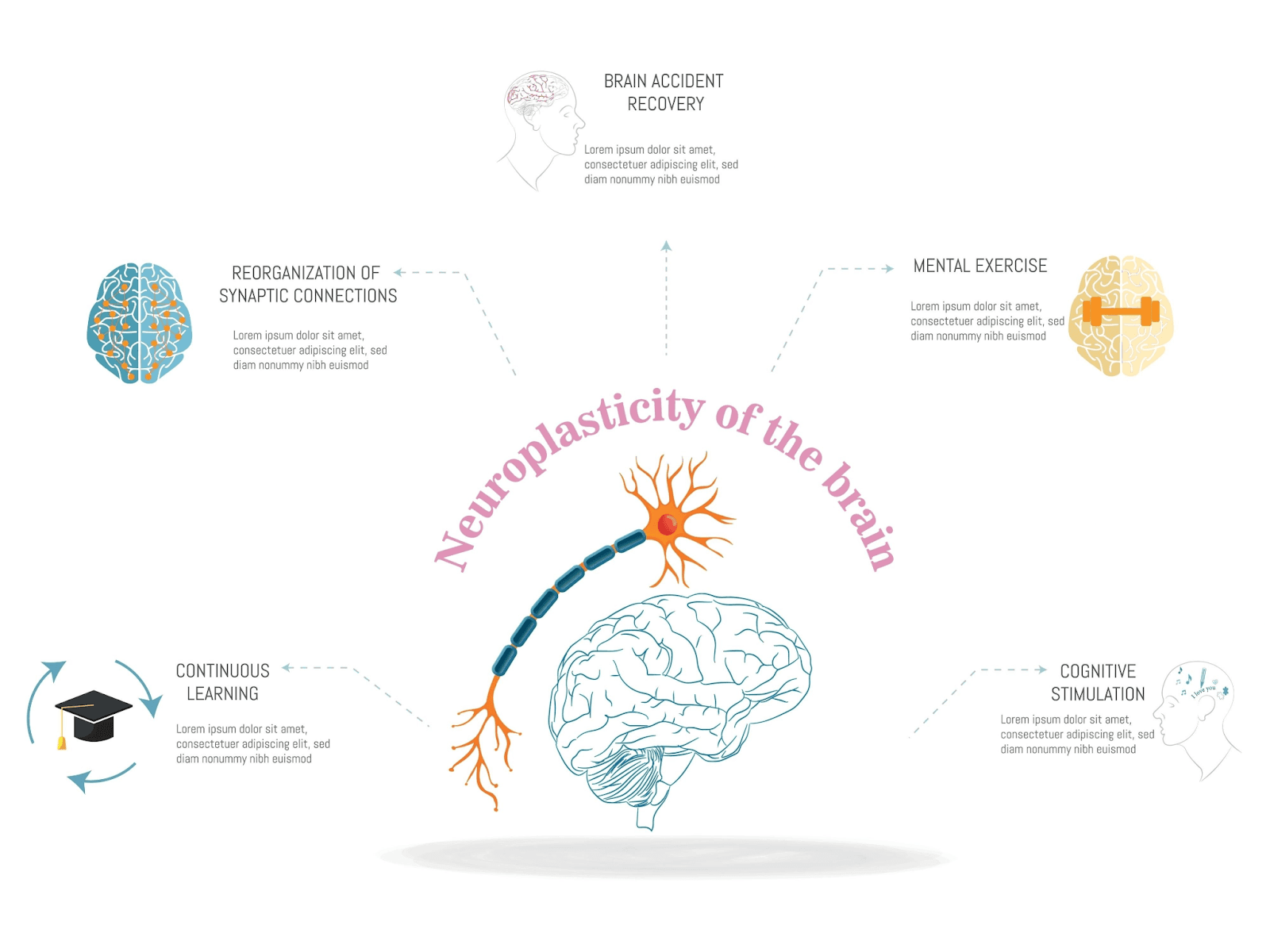
Components of Modern Neurorehabilitation
1. Technology-Assisted Therapy
Robotics: Robotic exoskeletons help paralyzed patients walk, providing the high-repetition training needed to rewire the brain.
Virtual Reality (VR): VR creates immersive environments for balance training and cognitive rehabilitation, making therapy engaging and fun.
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI): Allowing patients to control devices with their thoughts.
2. The Human Touch
Technology is a tool, but the human element is the driver.
Multidisciplinary Teams: Neurologists, physiatrists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and psychologists working together.
Patient-Centric Care: Tailoring the program to the patient's specific goals, whether it's walking to the mailbox or playing the piano again.
Dr. Sharan Srinivasan: A Case Study in Innovation
Dr. Sharan Srinivasan’s work in Bangalore exemplifies this modern approach.
PRS Neurosciences: His initiative focuses on making world-class rehabilitation accessible.
Newro LOGICS: Using computer-aided programs to map and train the brain, addressing cognitive deficits that are often ignored.
Holistic Philosophy: He treats the patient, not just the scan. This includes addressing depression, nutrition, and family dynamics.
The Future is Bright
The future of neurorehabilitation holds immense promise:
Stem Cell Therapy: Potential to regenerate damaged nerve tissue.
Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation: Using magnetic pulses (TMS) to "wake up" dormant brain areas.
Tele-Rehab: Bringing specialized therapy to patients in remote areas via video calls and sensors.
Key Takeaways
Hope is scientific: Recovery is biological, driven by targeted stimulation.
It takes a village: Recovery requires a team of experts and a supportive family.
Innovation saves lives: New tech is allowing recovery that was considered impossible 20 years ago.
Access matters: Leaders in the field are fighting to make these advanced therapies available to everyone, not just the wealthy.
FAQ
Q: How long does neurorehab take?
A: It is a marathon, not a sprint. It can take months or years, and for progressive conditions, it is a lifelong commitment.
Q: Is it expensive?
A: It can be, but many centers and NGOs (like Swaasthya Aarogya Foundation) are working to provide affordable options.
Q: Can old injuries be treated?
A: Yes. While early intervention is best, neuroplasticity can occur years after an injury with the right intensity of training.
Neurorehabilitation is the specialized process of helping patients recover from nervous system injuries (stroke, TBI, spinal cord injury) or manage progressive neurological diseases (Parkinson’s). It combines medical expertise with cutting-edge technology (robotics, brain mapping) and compassionate care. The goal is not just medical stability, but the restoration of function, independence, and dignity. Visionaries like Dr. Sharan Srinivasan are leading this field by integrating holistic care with advanced science.
The New Era of Recovery
In the past, a severe stroke or brain injury often meant a life of permanent dependency. Today, the field of neurorehabilitation is rewriting that narrative. It operates on the principle of Neuroplasticity—the brain's incredible ability to reorganize itself, form new connections, and compensate for injury.

Components of Modern Neurorehabilitation
1. Technology-Assisted Therapy
Robotics: Robotic exoskeletons help paralyzed patients walk, providing the high-repetition training needed to rewire the brain.
Virtual Reality (VR): VR creates immersive environments for balance training and cognitive rehabilitation, making therapy engaging and fun.
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI): Allowing patients to control devices with their thoughts.
2. The Human Touch
Technology is a tool, but the human element is the driver.
Multidisciplinary Teams: Neurologists, physiatrists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and psychologists working together.
Patient-Centric Care: Tailoring the program to the patient's specific goals, whether it's walking to the mailbox or playing the piano again.
Dr. Sharan Srinivasan: A Case Study in Innovation
Dr. Sharan Srinivasan’s work in Bangalore exemplifies this modern approach.
PRS Neurosciences: His initiative focuses on making world-class rehabilitation accessible.
Newro LOGICS: Using computer-aided programs to map and train the brain, addressing cognitive deficits that are often ignored.
Holistic Philosophy: He treats the patient, not just the scan. This includes addressing depression, nutrition, and family dynamics.
The Future is Bright
The future of neurorehabilitation holds immense promise:
Stem Cell Therapy: Potential to regenerate damaged nerve tissue.
Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation: Using magnetic pulses (TMS) to "wake up" dormant brain areas.
Tele-Rehab: Bringing specialized therapy to patients in remote areas via video calls and sensors.
Key Takeaways
Hope is scientific: Recovery is biological, driven by targeted stimulation.
It takes a village: Recovery requires a team of experts and a supportive family.
Innovation saves lives: New tech is allowing recovery that was considered impossible 20 years ago.
Access matters: Leaders in the field are fighting to make these advanced therapies available to everyone, not just the wealthy.
FAQ
Q: How long does neurorehab take?
A: It is a marathon, not a sprint. It can take months or years, and for progressive conditions, it is a lifelong commitment.
Q: Is it expensive?
A: It can be, but many centers and NGOs (like Swaasthya Aarogya Foundation) are working to provide affordable options.
Q: Can old injuries be treated?
A: Yes. While early intervention is best, neuroplasticity can occur years after an injury with the right intensity of training.
Neurorehabilitation is the specialized process of helping patients recover from nervous system injuries (stroke, TBI, spinal cord injury) or manage progressive neurological diseases (Parkinson’s). It combines medical expertise with cutting-edge technology (robotics, brain mapping) and compassionate care. The goal is not just medical stability, but the restoration of function, independence, and dignity. Visionaries like Dr. Sharan Srinivasan are leading this field by integrating holistic care with advanced science.
The New Era of Recovery
In the past, a severe stroke or brain injury often meant a life of permanent dependency. Today, the field of neurorehabilitation is rewriting that narrative. It operates on the principle of Neuroplasticity—the brain's incredible ability to reorganize itself, form new connections, and compensate for injury.

Components of Modern Neurorehabilitation
1. Technology-Assisted Therapy
Robotics: Robotic exoskeletons help paralyzed patients walk, providing the high-repetition training needed to rewire the brain.
Virtual Reality (VR): VR creates immersive environments for balance training and cognitive rehabilitation, making therapy engaging and fun.
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI): Allowing patients to control devices with their thoughts.
2. The Human Touch
Technology is a tool, but the human element is the driver.
Multidisciplinary Teams: Neurologists, physiatrists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and psychologists working together.
Patient-Centric Care: Tailoring the program to the patient's specific goals, whether it's walking to the mailbox or playing the piano again.
Dr. Sharan Srinivasan: A Case Study in Innovation
Dr. Sharan Srinivasan’s work in Bangalore exemplifies this modern approach.
PRS Neurosciences: His initiative focuses on making world-class rehabilitation accessible.
Newro LOGICS: Using computer-aided programs to map and train the brain, addressing cognitive deficits that are often ignored.
Holistic Philosophy: He treats the patient, not just the scan. This includes addressing depression, nutrition, and family dynamics.
The Future is Bright
The future of neurorehabilitation holds immense promise:
Stem Cell Therapy: Potential to regenerate damaged nerve tissue.
Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation: Using magnetic pulses (TMS) to "wake up" dormant brain areas.
Tele-Rehab: Bringing specialized therapy to patients in remote areas via video calls and sensors.
Key Takeaways
Hope is scientific: Recovery is biological, driven by targeted stimulation.
It takes a village: Recovery requires a team of experts and a supportive family.
Innovation saves lives: New tech is allowing recovery that was considered impossible 20 years ago.
Access matters: Leaders in the field are fighting to make these advanced therapies available to everyone, not just the wealthy.
FAQ
Q: How long does neurorehab take?
A: It is a marathon, not a sprint. It can take months or years, and for progressive conditions, it is a lifelong commitment.
Q: Is it expensive?
A: It can be, but many centers and NGOs (like Swaasthya Aarogya Foundation) are working to provide affordable options.
Q: Can old injuries be treated?
A: Yes. While early intervention is best, neuroplasticity can occur years after an injury with the right intensity of training.

